Human Apolipoprotein AI (Apo AI) | ABMC-P03
- SKU:
- ABMC-P03
- Availability:
- Usually shipped in 5 working days
Description
Human Apolipoprotein AI (Apo AI) | ABMC-P03
| Concentration: | 1 mg / ml, determined by the Lowry method |
| Source: | From fresh human plasma that has tested negative for Hepatitis C, HIV-I and HIV-II antibodies as well as Hepatitis surface antigens. |
| Purification: | After series ultracentrifugations, High Density Lipoprotein (HDL) is isolated from human plasma. Apo AI is purified from delipidated HDL, followed by gel-filtration. |
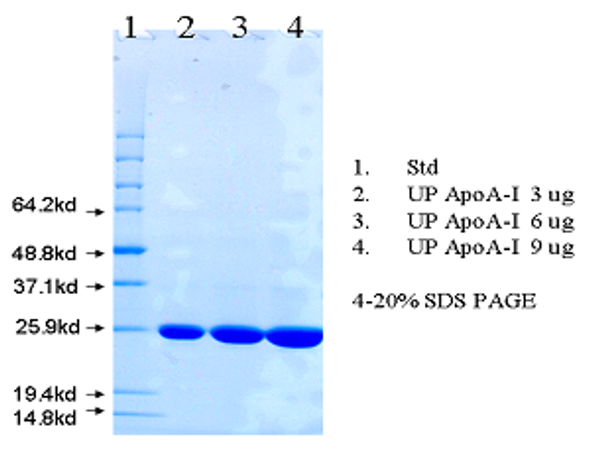
| Purity: | ≥ 98% by SDS-PAGE |
| Buffer: | 20 mM Tris-HCl, 140 mM NaCl, 0.02% NaN3, 0.5 mM EDTA, pH 7.4. |
| Storage: | -20°C for long-term storage, 4°C for short- term storage. Aliquot to avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
IMPORTANCE
Apo AI comprises approximately 70% of the protein moiety in HDL. It is a single polypeptide chain consisting of 243 amino acid residues without disulfide bound and with glutamic acid as the C-terminal residue and aspartic acid as the N-terminal residue. The molecular weight is reported to be 28 kDa (Brewer et al., 1978).
The roles of Apo AI in HDL function include reverse cholesterol transportation, lipid cholesterol binding, lecithin-cholesterol acyl transferase (LCAT) activation, and receptor binding, which is responsible for cholesterol esterification in plasma. Besides participate in cholesterol metabolism, Apo AI and HDL also suppress neutrophil activation, inhibit bacterial endotoxin, induce trypanosomal lysis, and other physiological activities. (Brouillette et al., 2001)
Apo AI levels may be inversely related to the risk of coronary disease. In previous research, Apo AI may affect diet-induced inflammation by either directly or indirectly altering lipid rafts. (Cheng et al., 2012)