ChonBlock™ Elisa & WB Blocking Buffers
ChonBlock™ ELISA Buffer
1. Published antibody assay data typically does not subtract false positive reactions caused by samples (background noise reaction).
2. This background (BG) noise reaction caused by the hydrophobic binding of immunoglobulin components in sample specimens to plastic surfaces is intense and can exceed the real antibody-antigen reaction.
3. No current blocking agents are capable of preventing this BG noise reaction, although they reduce the blank (BL) values caused by detection antibodies.
ELISAs are widely used to assay antibodies without serious consideration for false positive reactions attributed to the high binding affinity of proteins to plastic surfaces. Among the various non-specific reactions, BL values caused by detection antibodies are considered by all ELISA users, but most BG noise reactions caused by the samples themselves are often ignored. BG noise reactions are unique to individual samples and vary significantly depending on samples. Without considering this concept, BG noise reaction is included in data and misinterpreted, leading to numerous uncertain conclusions (1). It is imperative to recognize the various types of false reactions involved in ELISAs and to reinvestigate ELISA data to dispel the accumulated misinformed conclusions for future studies on antibodies in biological and medical fields.
Illustration of BG Noise Reaction Effects on Antibody Assay Data in ELISA
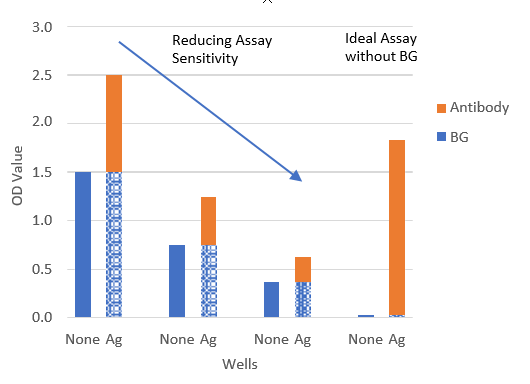
At low serum dilution, the BG noise reaction caused by the sample itself in antigen-coated wells (Ag) is intense and can exceed the antibody-antigen reaction. The BG noise reaction unique to individual samples can be easily determined in antigen uncoated (None) wells, but this step is often ignored.
NOTE: Attempts to reduce the BG noise reaction by reducing assay sensitivity do not reduce the BG noise reaction rate.
A newly developed buffer system, ChonBlock™, effectively prevents non-specific reactions involved in antibody ELISAs without affecting the antibody-antigen reaction. ChonBlock™ is useful for assaying antibodies against potential pathogenic environmental agents in human and animal sera, for determining the efficacy of various vaccines, and for studying immune function in patients with autoimmune diseases (1).
Preventing False Positive BG Noise Reactions with ChonBlock™
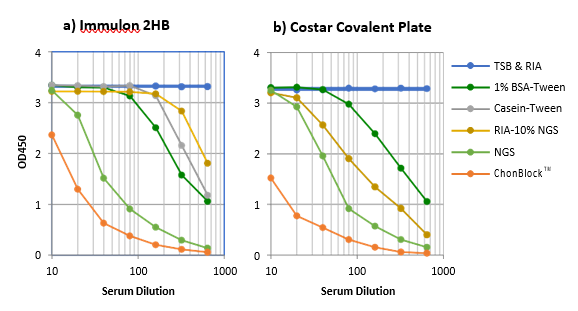
Serum from a patient with RA was serially diluted from 1/10 to 1/640 with individual buffers and added to antigen non-coated plain wells. IgG bound to the plastic surfaces was determined with HRP-conjugated anti-human IgG antibodies.
NOTE: ChonBlock™ effectively blocks BG noise reaction, whereas all current buffer systems fail to prevent it.
Assaying Anti-Cyclic Citrullinated Peptide (CCP) Antibodies
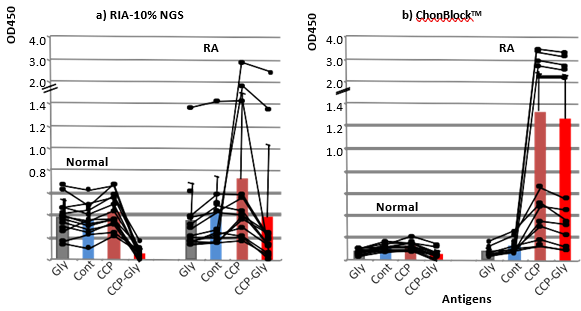
Serum samples from 13 normal controls and 13 patients with RA were diluted at 1/500 with a) RIA-10% NGS and
b) ChonBlock™ buffer, and added to Glycine (Gly), control peptide (Cont) and CCP-coupled wells (CCP). The OD values in CCP-wells were corrected by subtracting the BG noise OD values obtained in Gly-wells to obtain true OD values reflecting anti-CCP antibodies (CCP-Gly).
NOTE: In the RIA-10% NGS buffer system, anti-CCP antibodies were not determined due to the high BG noise reaction.
ChonBlock™ Western Blot Buffers
Traditional western blot buffers (BSA, Casein, NGS) provide an economical method for increasing the signal-to-noise ratio in a western blot. Many proprietary western blot buffers are more costly than these methods, but provide substantial blocking effects. ChonBlock™ is a new western blot buffer that proves to be just as capable as other proprietary buffers and at a cost-effective price.
1. Comparing the Effectiveness of ChonBlock™ to Common Western Blot Buffers
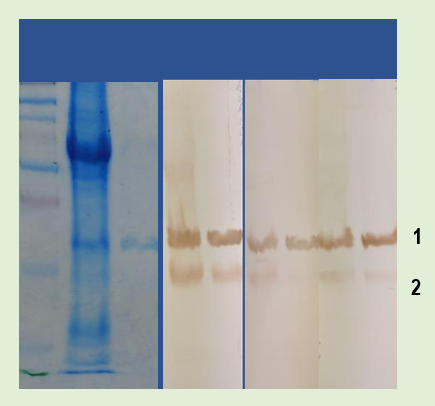
A western blot was run using a 15% poly-Acrylamide gel under reducing conditions to compare three different buffer systems. Mouse Anti-HMGB1
1 : monoclonal antibody (Clone 1-1.2BP1) was used as the primary antibody at 1
µg/ml, and goat anti-mouse IgG antibody conjugated with HRP was used as
2 : the secondary antibody at a 1/4000 dilution. A non-specific smear signal was observed in the BSA-Tween buffer due to the lack of blocking effect. The competitor’s buffer prevented non-specific smearing, but showed a weak signal with high background color. In contrast, a distinct HMGB1 band with low background was observed using ChonBlock™.
|
BSA |
Competitor |
ChonBlock™ |
|
|
Sensitivity |
Good |
Poor |
Good |
|
BG Noise |
Significant |
None |
None |
|
Specificity |
Low |
High |
High |
|
Price |
$ |
$$$ |
$$ |
2. Comparing the Effectiveness of ChonBlock™ to Competitor Western Blot Buffers
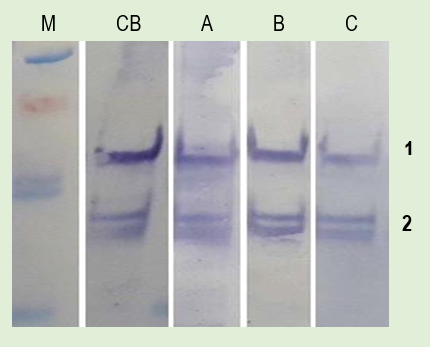
M: Molecular Marker
CB: ChonBlock™
A: Competitor’s Buffer A
B: Competitor’s Buffer B
C: Competitor’s Buffer C
1: HMGB1
2: Degraded HMGB1
Reagents:
• Sample: Cell lysate containing purified HMGB1
• Primary antibody: anti-HMGB1 mAb (Clone 1-1.2BP1, 1 μg/ml)
• Secondary antibody: goat anti-mouse IgG HRP (1:5000 dilution)
|
ChonBlock™ |
Competitor A |
Competitor B |
Competitor C |
|
|
Signal |
High |
Moderate |
Moderate |
Low |
|
Background Noise |
Low |
Low |
None |
None |
The Blocking Effectiveness of ChonBlock™ and 5% BSA-0.05% Tween 20 on BG Noise Reactions
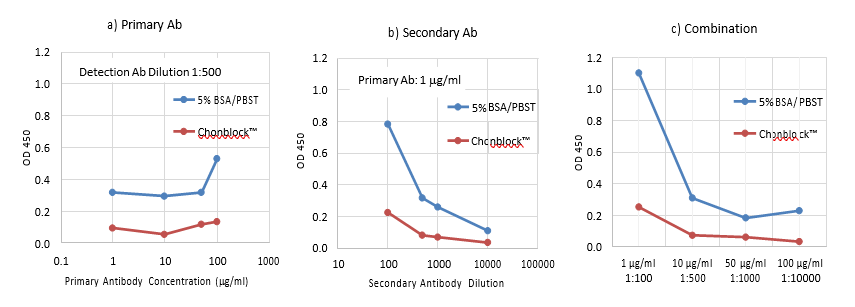
The background (BG) noise reaction in western blotting is caused by non-specific hydrophobic binding of antibodies to the nitrocellulose membrane. To determine the blocking ability of ChonBlock™ as compared to a conventional blocking buffer, small nitrocellulose membrane pieces were blocked with either ChonBlock™ or BSA-Tween and reacted with primary and secondary antibodies in an ELISA plate. Color was developed using soluble TMB and OD values for each well were quantitatively obtained using a plate reader. As seen in the above graphs, the BG noise OD values depend on antibody concentration (a & b) and consequently are enhanced by their combination (c). ChonBlock™ prevents BG noise reaction more effectively than BSA.
|
Catalog # |
Description |
|
ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-1 for Blocking/Primary Antibody Dilution (x100 concentrate), 10 ml |
|
|
ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-2 for Goat Secondary Antibody Dilution (x100 concentrate), 10 ml |
|
|
ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-2 for Rabbit Secondary Antibody Dilution (x100 concentrate), 10 ml |
|
Western Blot Protocol: Choose PBS or TBS-based Chonblock™ based on your study needs.
1. Prepare a 1X ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-1 solution by diluting with PBS or TBS.
2. Block membrane with 1X ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-1 at room temperature for 1 hour.
3. Prepare the primary antibody solution by diluting with 1X ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-1.
NOTE: Optimize the primary antibody concentration before use.
4. Incubate the membrane in the primary antibody solution at 4°C overnight.
5. Wash the membrane with PBS-Tween or TBS-Tween for 5 minutes, 3 times.
6. Prepare 1X ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-2 by diluting with PBS or TBS.
7. Prepare the HRP-conjugated secondary antibody solution by diluting with 1X ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-2.
NOTE 1: Choose ChonBlock™ WB Buffer-2 for goat or rabbit depending on the secondary antibody’s origin.
NOTE 2: Use secondary antibodies pre-adsorbed against the same species as the sample. NOTE 3: Optimize the secondary antibody concentration before use.
8. Incubate the membrane in the HRP-conjugated secondary antibody solution at room temperature for 1 hour.
9. Wash the membrane with PBS-Tween or TBS-Tween for 5 minutes, 3 times.
10. Develop bands using desired chromogen, DAB or TMB.
11. Rinse the membrane with distilled water.
