Unlocking Precision in Molecular Biology : Maxanim and Gentaur’s Deep Dive into Digital PCR Applications and Techniques
In the fast-evolving landscape of molecular diagnostics and genomics, digital PCR stands out as a transformative technology. Renowned for its precision and sensitivity, digital PCR (dPCR) empowers researchers to quantify nucleic acids with absolute accuracy. Whether you’re leveraging digital PCR for gene expression analysis, troubleshooting low yields, or exploring its cutting-edge applications, this blog post dives into its technical nuances and practical uses. Let’s explore how dPCR is reshaping research and diagnostics.
What is Digital PCR ? A Quick Overview
Digital PCR is an advanced nucleic acid quantification technique that partitions a sample into thousands of individual reactions, enabling absolute quantification of DNA or RNA. By counting the number of positive partitions via fluorescence, dPCR delivers precise results, making it ideal for applications like digital PCR for single-cell sequencing or detecting rare mutations. Its ability to provide absolute counts without standard curves sets it apart in molecular biology. PMID: 26521179
Key Applications of Digital PCR
- Digital PCR for Gene Expression Analysis
Measuring gene expression with dPCR provides absolute counts of RNA molecules, offering unmatched precision. This is especially valuable in cancer studies or developmental biology, where accurate quantification drives discovery.
- Reference: PMID: 24740231
- Digital PCR for Single-Cell Sequencing
Pairing dPCR with single-cell analysis enables quantification of DNA or RNA at the cellular level, providing insights into tumor heterogeneity or stem cell dynamics. - Reference: PMID: 38391989
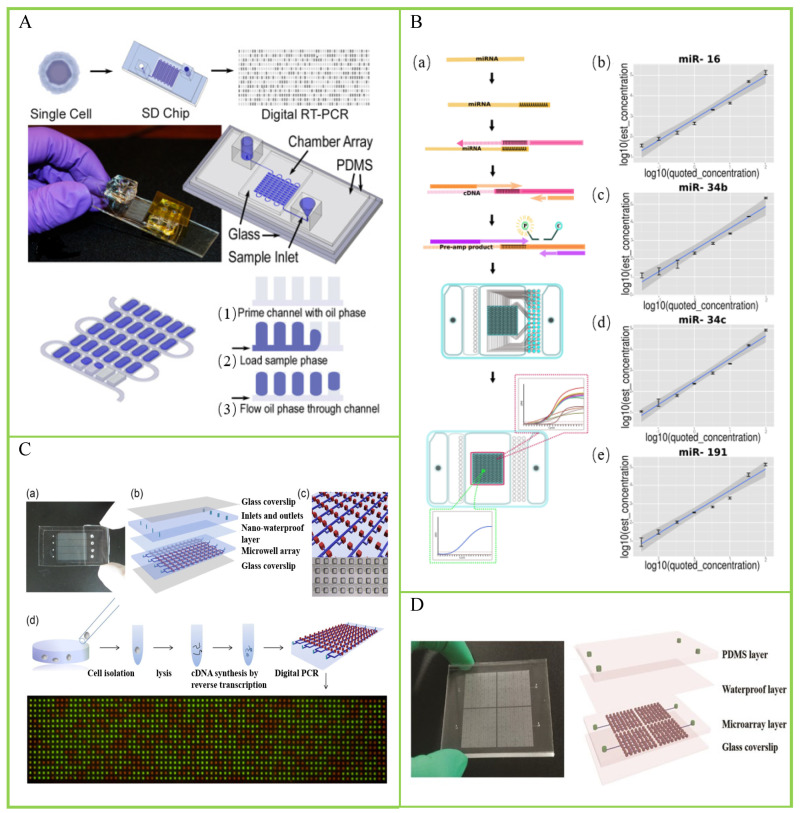
- Digital PCR Protocols for Cancer Research
In cancer genomics, dPCR shines at detecting rare mutations or copy number variations. Its precision supports biomarker identification and monitoring of minimal residual disease.
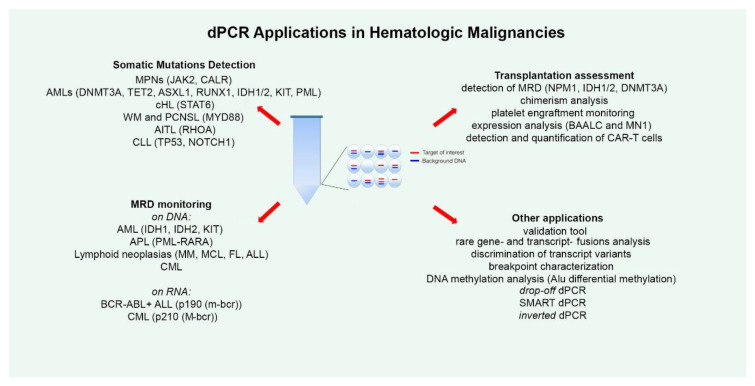
- Reference: PMID: 32354129
Building Your Digital PCR Workflow
For those new to the technique, mastering the digital PCR workflow for beginners is key. The process typically involves:
- Sample preparation: Dilute your DNA or RNA to optimize partitioning.
- Partitioning: Use a dPCR system (e.g., droplet-based or chip-based) to divide the sample into thousands of reactions.
- Amplification: Run the PCR reaction in each partition.
- Detection: Analyze positive vs. negative partitions using fluorescence.
A)
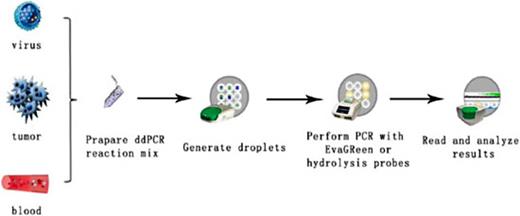
B)
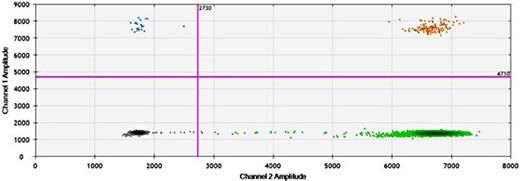
Looking for specifics ? Digital PCR kits for RNA quantification, available through suppliers like Maxanim, streamline this process with pre-optimized reagents tailored for RNA targets. Challenges like digital PCR troubleshooting low yield can occur—often due to suboptimal sample concentration or primer design. Adjusting input DNA or using validated digital PCR primers for rare mutations can mitigate these issues.
Choosing the Right Tools
Selecting the best digital PCR machines for small labs is critical for efficient research, and suppliers like us offer a range of cutting-edge solutions. For instance, Gentaur’s digital PCR systems, distributed by Maxanim, provide compact, high-performance options ideal for labs with limited space. These systems feature advanced droplet-based technology, ensuring precise partitioning and reliable results for applications like digital PCR for gene expression analysis.
Why Digital PCR Matters in 2025
The digital PCR sensitivity for low DNA samples and its versatility across applications—from viral detection to cancer research—make it a cornerstone of precision medicine. As costs decrease and accessibility improves, small labs and educational settings may increasingly adopt dPCR. Whether you’re refining digital PCR protocols for cancer research or exploring digital PCR for gene expression analysis, this technology offers a window into the molecular world with exceptional clarity.
- Reference: PMCID: PMC6010488
Digital PCR isn’t just a tool—it’s a paradigm shift in molecular biology. Its ability to deliver absolute quantification, paired with applications spanning single-cell sequencing to RNA quantification, positions it at the forefront of modern research. Ready to dive in? Explore the best digital PCR machines for small labs through trusted suppliers like Maxanim, optimize your workflow, and unlock the power of precision. Have questions or need help with digital PCR troubleshooting low yield? Drop a comment below—we’re here to assist!
Digital PCR vs. Real-Time PCR: Understanding the Difference
While both digital PCR (dPCR) and real-time PCR (qPCR) amplify and detect nucleic acids, their approaches differ fundamentally. Digital PCR partitions the sample into thousands of reactions, counting positive partitions for absolute quantification—ideal for digital PCR sensitivity for low DNA samples or rare mutation detection. Real-time PCR, by contrast, monitors amplification in real time using fluorescence thresholds (Ct values), relying on standard curves for relative quantification. This makes qPCR faster and suited for high-throughput screening, but less precise for low-abundance targets compared to dPCR’s robust, partition-based accuracy.
- Reference: PMCID: PMC4706846
Recent Posts
-
Nicholas E. Navin’s Keynote on Breast Cancer at SCSOmics 2025 (with Lieven in Attendance)
At SCSOmics 2025, held earlier this year, Nicholas E. Navin, PhD, delivered a keynote address that d …17th Sep 2025 -
Reflections on Our Experience at the Vatican Longevity Summit
On March 24, 2025, the Vatican opened its doors to a remarkable gathering of scientists, ethicists, …25th Mar 2025 -
Gentaur : The Leading Distributor of Applied Biological Materials (ABM) in Belgium and Europe
Driving Scientific Innovation with ABM's Cutting-Edge Products Gentaur has long been the trusted dis …19th Mar 2025




