dPCR vs ddPCR ddPCR vs qPCR digital PCR vs qPCR
dPCR vs ddPCR ddPCR vs qPCR digital PCR vs qPCR
Modern molecular biology uses several PCR technologies for DNA and RNA analysis. The most common comparisons researchers search online include:
dPCR vs qPCR
ddPCR vs qPCR sensitivity
digital PCR vs qPCR
droplet digital PCR vs qPCR
qPCR vs PCR
digital PCR vs real time PCR
Understanding the difference between PCR technologies helps laboratories choose the right method for accurate detection, quantification, and research applications.
This guide explains digital PCR, droplet digital PCR, qPCR, and how they compare in sensitivity, accuracy, and performance.
what is PCR
PCR stands for Polymerase Chain Reaction. It is a method used to amplify DNA so it can be detected and analyzed.
PCR is widely used in:
diagnostics
gene detection
sequencing
molecular biology research
Traditional PCR is mainly qualitative. It detects DNA but does not measure precise quantity. This limitation led to the development of qPCR and digital PCR technologies.
qpcr full form and what is qpcr
The qPCR full form is quantitative polymerase chain reaction. It is also called real time PCR or q PCR.
Common search questions include:
what is qPCR
what is qPCR used for
what does qPCR measure
qPCR measures fluorescence during amplification cycles to estimate the amount of DNA present in a sample.
what is qpcr used for
qPCR is widely used for:
gene expression analysis
pathogen detection
viral load measurement
clinical diagnostics
research quantification
qPCR provides relative quantification based on amplification curves and standard references.
what does qpcr measure
qPCR measures fluorescence signals generated during DNA amplification. These signals correlate with DNA concentration but depend on reaction efficiency and calibration standards.
This is why researchers often compare qPCR vs digital PCR for more precise quantification.
rt pcr vs qpcr and qpcr vs rt pcr
RT PCR converts RNA into DNA before amplification.
qPCR quantifies DNA during amplification.
RT PCR vs qPCR difference:
RT PCR detects RNA presence
qPCR measures DNA quantity
Many workflows combine both steps for RNA quantification.
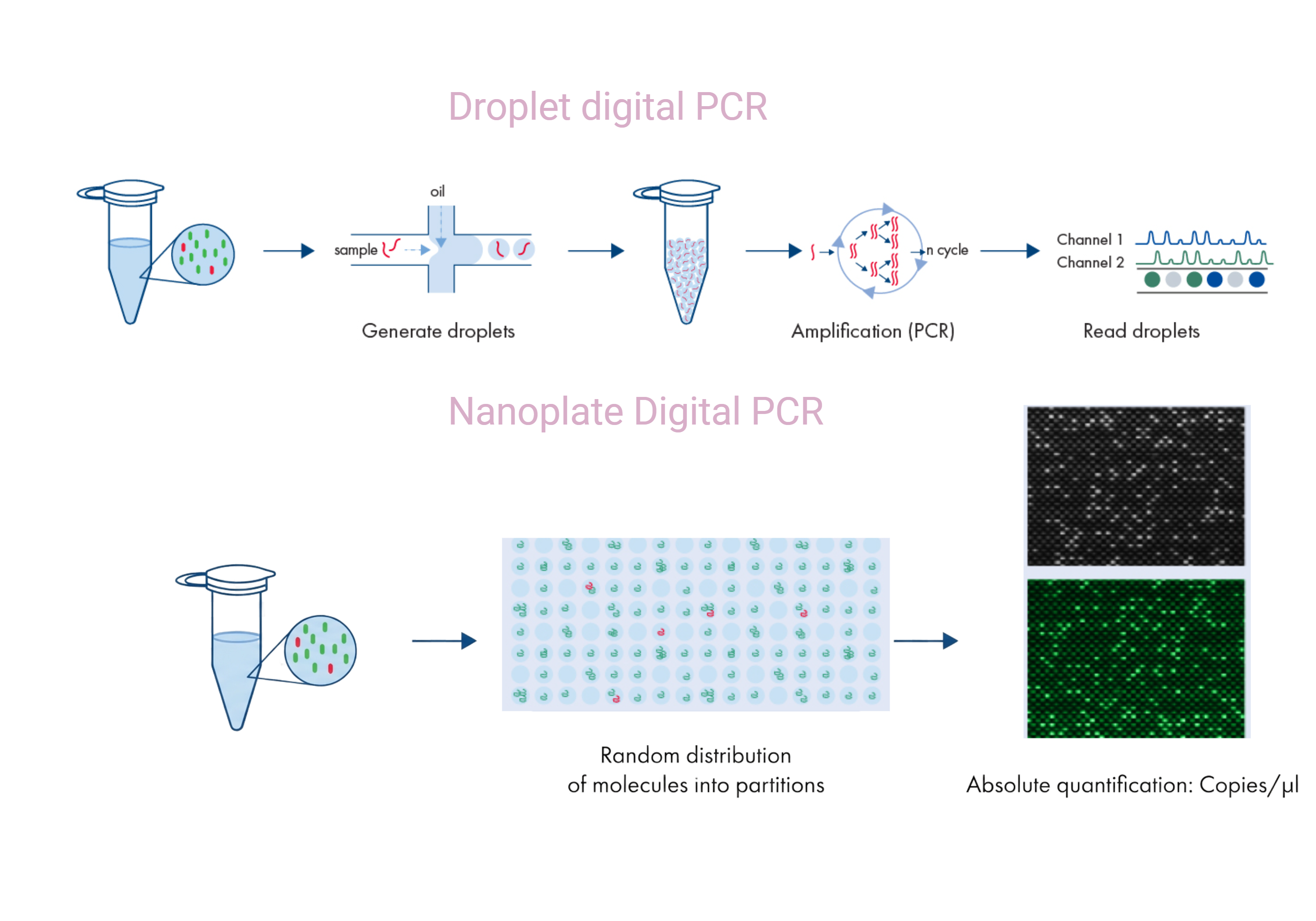
digital pcr explained and what is digital pcr
Digital PCR explained simply:
Digital PCR partitions a sample into thousands of small reactions. Each partition is analyzed individually to determine whether DNA is present or absent.
By counting positive partitions, digital PCR calculates absolute DNA copy number.
Common search terms include:
digital PCR
digital qPCR
dpcr system
digital PCR vs real time PCR
dpcr system
A dpcr system divides the sample into many microreactions and performs amplification in each partition.
Digital PCR systems provide:
absolute quantification
high sensitivity
rare mutation detection
precise copy number measurement
ddpcr vs dpcr and digital pcr vs droplet digital pcr
ddPCR stands for droplet digital PCR.
Difference:
digital PCR = general technology
droplet digital PCR = droplet-based implementation
In ddPCR, the sample is divided into thousands of oil droplets before amplification.
Important concept:
All ddPCR is digital PCR, but not all digital PCR uses droplets.
digital PCR vs qPCR and dpcr vs qpcr and qpcr vs dpcr
This is one of the most important comparisons.
qPCR:
relative quantification
depends on standard curves
digital PCR:
absolute quantification
counts DNA molecules directly
Digital PCR provides higher precision, especially for low DNA concentrations.
ddpcr vs qpcr sensitivity
ddPCR vs qPCR sensitivity is a major reason laboratories adopt digital PCR.
ddPCR detects:
rare mutations
very low copy targets
minimal fold changes
Digital partitioning reduces amplification bias and improves detection accuracy.
droplet digital pcr vs qpcr and digital droplet pcr vs qpcr
Droplet digital PCR vs qPCR differences include:
ddPCR advantages:
absolute measurement
higher sensitivity
no calibration curve
better reproducibility
qPCR advantages:
faster workflow
high throughput
lower cost
digital PCR vs real time PCR and real time PCR vs digital PCR
Real time PCR measures DNA amplification continuously.
Digital PCR counts molecules individually.
Digital PCR is more precise for:
copy number variation
mutation detection
low abundance targets
qpcr vs pcr and pcr vs qpcr
PCR vs qPCR difference:
PCR detects DNA presence.
qPCR measures DNA quantity.
qPCR adds real-time monitoring to traditional PCR amplification.
ddpcr vs pcr
ddPCR vs PCR comparison shows that droplet digital PCR provides quantitative and highly sensitive detection, while conventional PCR is mainly qualitative.
advantages and disadvantages of pcr
Advantages
rapid DNA amplification
widely available
versatile applications
Limitations
traditional PCR not quantitative
qPCR requires standards
digital PCR requires specialized instruments
summary of ddpcr vs qpcr vs dpcr
PCR technologies differ mainly in quantification accuracy.
PCR → DNA amplification
qPCR → relative quantification
dPCR → absolute quantification
ddPCR → droplet-based digital PCR
Digital PCR methods provide the highest precision for modern molecular biology.
commercial applications of digital pcr
Digital PCR is widely used in:
oncology testing
infectious disease detection
gene expression research
liquid biopsy analysis
sequencing validation
Many laboratories adopt digital PCR systems for high sensitivity and reproducibility.
