Description
Puromycin | ant-pr
Selective antibiotic for the Pac gene
Selection antibiotic: endotoxin tested, sterile reagent
Puromycin is an aminonucleoside antibiotic produced by Streptomyces alboniger. It specifically inhibits peptidyl transfer on both prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. This antibiotic inhibits the growth of Gram positive bacteria and various animal and insect cells.
Puromycin can also be used in some particular conditions for the selection of E. coli transformants. Resistance to puromycin is conferred by the Pac gene encoding a puromycin N-acetyl-transferase [1].
Animal cells are generally sensitive to concentrations from 1 to 10 µg/ml.
Specifications
Product concentration: 10 mg/ml
CAS number: 58-58-2
Quality Control: Each lot is thoroughly tested to ensure the absence of lot-to-lot variation.
Purity: ≥ 98% (HPLC)
Endotoxin level: < 5 EU/mg
Physicochemical characterization: pH, appearance
Cell-culture tested: potency validated in puromycin-sensitive and puromycin‑resistant mammalian cell lines
Non-cytotoxicity of trace contaminants: absence of long-term effects confirmed in puromycin-resistant cells
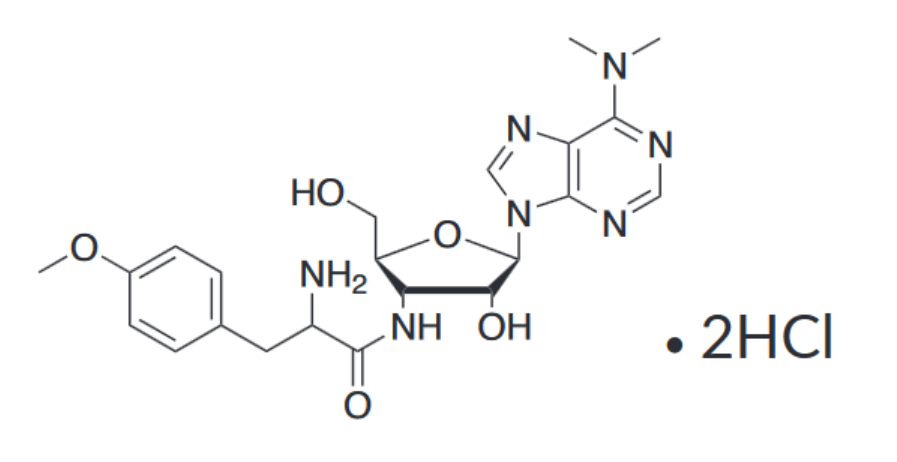
Formula: C22H29N7O5 • 2HCl
Molecular weight: 544.3
Structure :
Contents
Puromycin dihydrochloride is supplied as a sterile filtered solution at 10 mg/ml in HEPES buffer.
This product is available in three pack sizes:
- ant-pr-1: 10 x 1 ml (100 mg)
- ant-pr-5: 50 x 1 ml (500 mg)
- ant-pr-5b: 1 x 50 ml (500 mg)
Puromycin is shipped at room temperature.
Upon receipt it should be stored at 4°C or -20°C.
Puromycin is a harmful compound. Refer to safety data sheet for handling instructions.
Details
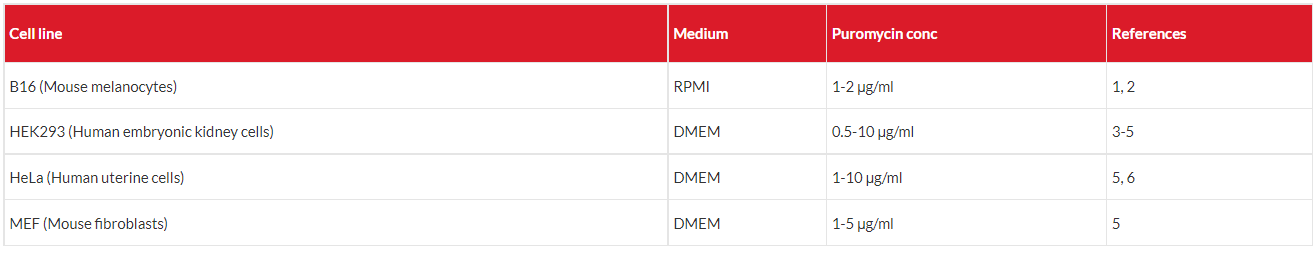
WORKING CONCENTRATIONS
The working concentrations of puromycin for mammalian cell lines range from 1 to 10 μg/ml.
In a starting experiment we recommend to determine optimal concentrations of antibiotic required to kill your host cell line.
Puromycin quickly kills eukaryotic cells that do not contain the pac gene. Dying cells detach from the plates, allowing easy and early identification of transformant clones.
Suggested working conditions for selection in some mammalian cells are listed below.