How Are Molecular Diagnostics and Genomic Technologies Revolutionizing Meningitis Research and Pathogen Detection?
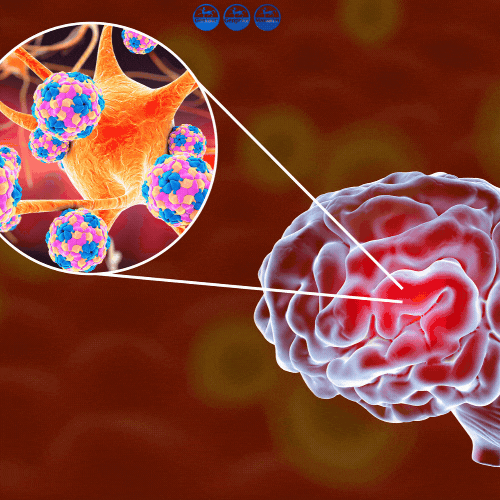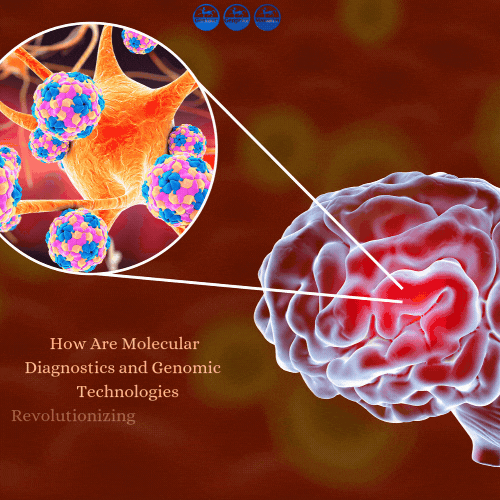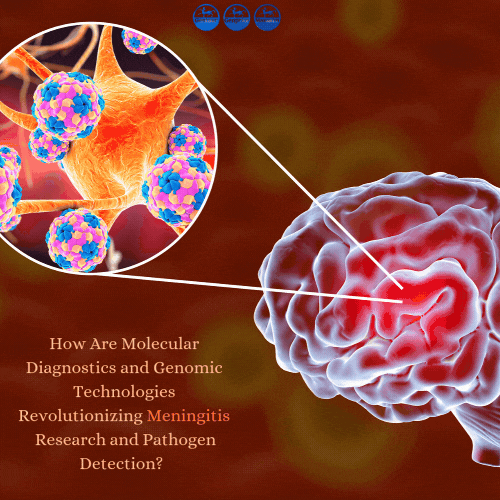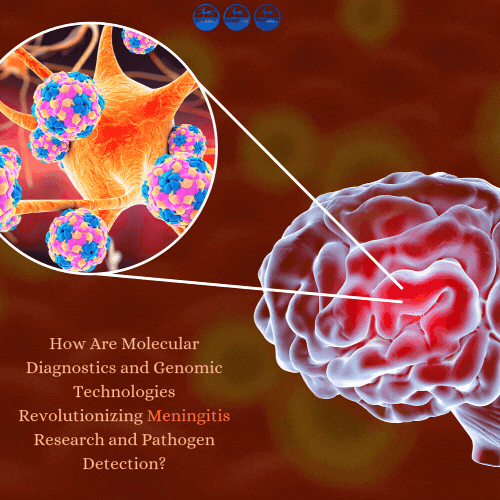
Meningitis remains a subject of profound scientific interest, encompassing a wide spectrum of pathogens and biological interactions. Researchers continue to explore its intricate mechanisms, ranging from host-pathogen interactions to the molecular evolution of causative agents. The advent of molecular diagnostics, particularly real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR), has not only improved detection efficiency but also opened new avenues for understanding biological dynamics.

Meningitis: A Multifaceted Challenge in Neuroscience and Microbiology
Meningitis, characterized by inflammation of the meninges, represents a significant challenge in both experimental and theoretical research. Its etiology spans bacterial, viral, fungal, and parasitic origins, with each category exhibiting unique biological patterns. While traditional culture-based methods have provided valuable insights, their limitations in speed and sensitivity have driven the demand for molecular advancements.
Beyond infectious agents, recent studies have also explored environmental and genetic factors influencing susceptibility. Understanding the full spectrum of this condition requires a multidisciplinary approach that integrates microbiology, genomics, and molecular biology.
The Molecular Perspective: Tracing Biological Markers with Precision
In the ever-evolving landscape of microbiological research, molecular techniques have emerged as essential tools for studying biological processes. Nucleic acid amplification technologies, including RT-PCR, enable researchers to delve into the genetic underpinnings of meningitis-associated organisms. Beyond mere identification, these approaches allow for:
- Genotypic Characterization:Understanding the genetic variations that influence biological traits.
- Epidemiological Mapping: Tracing patterns with precision, leading to more targeted research strategies.
- Host-Pathogen Interactions: Deciphering molecular interactions that influence biological responses.
- Molecular Evolution Studies: Investigating how microorganisms adapt over time, providing insights into biological changes.
The development of specialized RT-PCR kits, such as viral meningitis real-time PCR kits, has significantly enhanced the ability to detect and differentiate viral pathogens with high specificity. These tools offer researchers a streamlined approach to studying the genetic signatures of meningitis-causing viruses, allowing for more detailed molecular characterization and epidemiological investigations.
See related products:

Bridging Laboratory Research and Computational Biology
- From a research perspective, the study of meningitis extends beyond basic detection methods. The interplay between cellular responses, microbial strategies, and genetic predispositions continues to be an area of deep investigation. Molecular tools not only facilitate rapid identification but also contribute to broader research efforts in:
- Genomic Analysis: Refining data collection through advanced sequencing insights.
- Biomarker Discovery: Identifying novel indicators of biological activity and cellular responses.
- Comparative Genomics: Investigating genetic similarities and differences among various agents.
- Microbiome Influence: Studying how microbial communities interact with biological systems.
Emerging Frontiers in Meningitis Research
Recent studies highlight the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning in microbiological research, aiding in predictive modeling and pattern recognition. Additionally, advancements in sequencing technologies promise an era of unprecedented granularity in understanding biological interactions. Such innovations are expected to refine molecular research approaches and improve comprehension of environmental and genetic influences.
Another emerging field of interest is single-cell RNA sequencing, which allows researchers to examine how individual cells within biological systems respond to various stimuli. This approach provides new insights into cellular heterogeneity and could uncover novel biological markers.
Furthermore, the development of organ-on-a-chip models is providing new avenues for studying cellular interactions in a controlled environment. These microfluidic platforms enable researchers to mimic complex biological barriers, investigate molecular interactions, and test experimental compounds more effectively.
Read more....
The study of meningitis is at a fascinating crossroads, where traditional methodologies intersect with cutting-edge molecular technologies. As researchers continue to unravel the complexities of biological interactions, molecular tools provide not just analytical advantages but a deeper lens into intricate biological systems. The fusion of genomics, microbiology, and computational biology promises to elevate our understanding, ultimately paving the way for more refined research methodologies.
With the expanding role of computational tools and in-depth molecular studies, the next decade is set to bring remarkable discoveries that could redefine how researchers approach microbiological challenges. The scientific community must continue fostering interdisciplinary collaboration to translate these research advances into innovative methodologies.
Recent Posts
-
Nicholas E. Navin’s Keynote on Breast Cancer at SCSOmics 2025 (with Lieven in Attendance)
At SCSOmics 2025, held earlier this year, Nicholas E. Navin, PhD, delivered a keynote address that d …17th Sep 2025 -
Reflections on Our Experience at the Vatican Longevity Summit
On March 24, 2025, the Vatican opened its doors to a remarkable gathering of scientists, ethicists, …25th Mar 2025 -
Gentaur : The Leading Distributor of Applied Biological Materials (ABM) in Belgium and Europe
Driving Scientific Innovation with ABM's Cutting-Edge Products Gentaur has long been the trusted dis …19th Mar 2025



