Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains Kappa and Lambda Human ELISA | RD194088100R
- SKU:
- RD194088100R
- Availability:
- In Stock
- Regulatory status:
- RUO
- Type:
- Sandwich ELISA, HRP-labelled antibody
- Other names:
- FLC
- Species:
- Human
- Size:
- 2x 96 wells(1 kit)
Description
Immunoglobulin Free Light Chains Kappa and Lambda Human ELISA | RD194088100R
Features
- Intended for research use only.
- The total assays time is less than 3.5 hours.
- The kit measures FLC kappa and FLC lambda in serum, plasma and urine.
- Components of the kit are provided ready to use, concentrated and lyophilized.
- Calibrators and Quality Controls are human serum based.
Research topic
Autoimmunity, Oncology
Summary
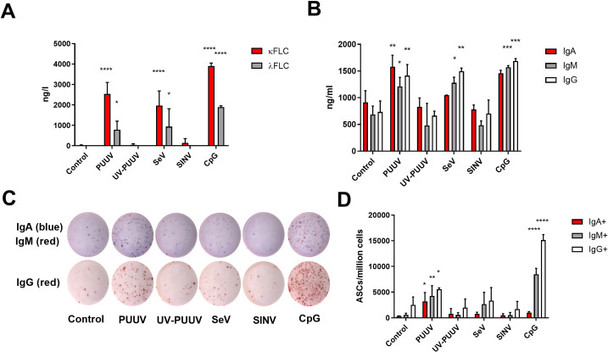
Human immunoglobulin molecules consist of two identical heavy chains which define immunoglobulin classes (IgG, IgA, IgM, IgD and IgE) and identical light chains (kappa or lambda) that are covalently linked to a heavy chain. In healthy individuals, the majority of light chains in serum exist bound to heavy chain. However, low levels of free light chains (FLCs) are found in serum of normal individuals due to their excess production over heavy chains by mature B-cells. In serum, FLC kappa exists predominantly as a monomer with a molecular weight of 22.5 kDa and FLC lambda as a dimer with a molecular weight of 45 kDa. This size difference results in a differential glomerular filtration rate and, consequently, a ratio of FLC kappa to FLC lambda of 1:1.6 in serum.
FLCs are observed in urine too but filtration and reabsorption of low molecular proteins in the kidney strongly affects the FLC concentration so that urinary FLC level is low in healthy individuals.
FLC are a natural product of B lymphocytes and, as such, represent a unique biomarker of neoplastic and reactive B cell-related disorders. Increased FLCs are associated with malignant plasma dyscrasia and other lymphocyterelated immunoproliferative disorders.
The detection of the FLCs is important diagnostic aid for a variety of monoclonal gammopathies, such as multiple myeloma, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia, nonsecretory myeloma, smoldering multiple myeloma, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. Accurate measurement of monoclonal free light chains in serum and/or urine is especially important in light-chain diseases, such as light-chain myeloma, primary systemic amyloidosis, and light chain-deposition disease. The ability to quantify monoclonal FLCs may be useful to monitor the disease. In patients with light chain myeloma, either of light chain, kappa or lambda, is dominantly produced and resulting in marked changes of the FLC κ/λ ratio in the early phase of the disease. The detection of urinary monoclonal kappa or lambda free light chains of immunoglobulin, also know as Bence Jones proteins (BJP), are important for identifying and monitoring Bcell malignancies too.
In addition, compared with the healthy state, the synthesis of polyclonal FLC is markedly increased in conditions associated with B cell activation as found in certain inflammatory or autoimmune diseases (e.g. systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis, or multiple sclerosis, as well as in cancer, diabetes mellitus, and AIDS).
Type
Sandwich ELISA, Biotin-labelled antibody
Applications
Serum, Plasma-EDTA, Plasma-Heparin, Plasma-Citrate, Urine
Sample Requirements
2×5 µl/well
Shipping
At ambient temperature. Upon receipt, store the product at the temperature recommended below.
Storage/Expiration
Store the kit at 2–8°C. Under these conditions, the complete kit is stable until the expiration date (see label on the box).
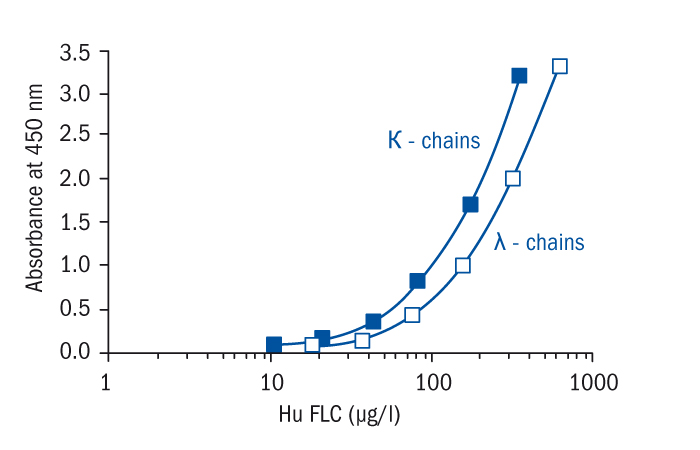
Calibration Curve
Calibration Range
10–320 µg/l (FLC kappa)
17.5–560 µg/l (FLC lambda)
Limit of Detection
FLC kappa ELISA Limit of detection (LOD) (defined as concentration of analyte giving absorbance higher than mean absorbance of blank plus three standard deviations of the absorbance of blank: Ablank + 3×SDblank) is calculated from the real FLC kappa values in wells and is 6 μg/L.
FLC lambda ELISA Limit of detection (LOD) (defined as concentration of analyte giving absorbance higher than mean absorbance of blank plus three standard deviations of the absorbance of blank: Ablank + 3×SDblank) is calculated from the real FLC lambda values in wells and is 5 μg/L.
Intra-assay (Within-Run)
n = 8;
CV = 3.0% (FLC kappa)
CV = 4.5% (FLC lambda)
Inter-assay (Run-to-Run)
n = 6;
CV = 7.0% (FLC kappa)
CV = 6.4% (FLC lambda)
Spiking Recovery
101.4% (FLC kappa)
100.9% (FLC lambda)
Dilution Linearity
87.8% (FLC kappa)
85.8% (FLC lambda)
Crossreactivity
- bovine Non-detectable
- cat Not tested
- goat Non-detectable
- horse Non-detectable
- dog Not tested
- hamster Not tested
- mouse Non-detectable
- pig Non-detectable
- rabbit Non-detectable
- rat Non-detectable
- sheep Non-detectable
- chicken Not tested
- monkey Not tested
- human Yes