Rabbit Polyclonal Antiserum Methionine AdenosylTransferase | PA00401-50
- SKU:
- ART-PA00401-50
- Availability:
- Usually Shipped in 5 Working Days
- Size:
- 50 µg
Description
Rabbit Polyclonal Antiserum Methionine AdenosylTransferase | PA00401-50 | Arthus Biosystems
Product name
Rabbit anti-MAT s, Rabbit anti-MAT g
Catalog Number
PA00401-50 (no glycerol), PA00402-50 (with glycerol)
Description
Rabbit polyclonal antiserum against methionine adenosyltransferase (MAT, E.C. 2.5.1.6)
Properties
Form
Liquid
Storage instruction
Store at 4°C if used within 1-2 weeks, store at below -20°C for long term
Storage buffer
Antiserum in PBS 10mM pH 7.4 (NaCI 150mM), sodium azide 0.02% (glycerol 50%)
Packaging
50 pl
Clonality
Rabbit polyclonal
Titer
— 1:420,000 (ELISA)
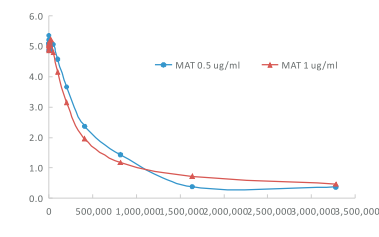
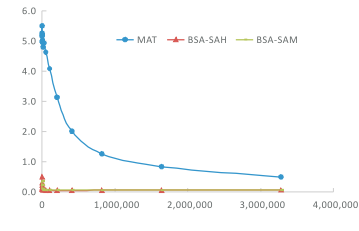
Specificity
SAM: S-adenosylmethionine, SAH: S-adenosylhomocysteine, BSA: Bovine Serum Albumin
Immunogen
recombinant MAT conjugated to KLH
Research Areas
- Methylation of biomolecules (DNA, RNA, proteins, hormones, neurotransmitters, etc.)
- One-carbon and mitochondria! metabolisms
- Signal transduction
- Epigenetics
- Pathways and processes
- Cancer and other disorders
Applications
The use of PA00401 or Pa00402 in the following applications has been tested. The application notes include recommended starting dilutions. Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. The product can be used in other applications such as IHC, Immunoprecipitation etc.
Notes
ELISA: 1:-120,000
Target
Except for parasites that rely on host for living, cells from all organisms have methionine adenyltransferase (MAT, EC2.5.1.6), also known as S-adenosylmethionine synthetase. MAT genes have been found to be exceptionally conserved throughout evolution. It was reported that there is 59% homology between human and E. coli MAT gene sequences. In mammals, three forms or isozymes of MAT have been identified that are encoded by three MAT genes. The MAT1a gene encodes al catalytic subunit. MAT-I is a tetramer of al subunits and MAT-III a dimer of the same subunits. Both MAT-I and MAT-III are present in adult liver cells. MAT-II is a heterotetramer formed by MAT2a encoding the catalytic subunit of a2 and MAT2b gene encoding regulatory 6 subunit, present in cells other than liver, embryonic liver and hepatoma cells. MAT catalytic reaction in the body is divided into two steps:
(1) Catalyze L- methionine (L-Met) and adenosine triphosphate (ATP) to generate S-adenosylmethionine (known as the active methionine, SAM) and tripolyphosphate (PPPi). Both SAM and PPPi remain on the surface of MAT at this stage.
(2)The phosphatase activity of MAT further decompose PPPi to dimeric phosphoric acid (PPi) and inorganic monophosphate (Pi). SAM can only be synthesized by MAT. SAM is one of the few sulfur-containing active substances that carry extre mely diverse and important biological functions in nature and is the key molecules in the methionine cycle.
Cellular localization: cytoplasm, nucleus