anti-Polyglutamylation Modification, mAb (GT335) | AG-20B-0020-C100
- SKU:
- AG-20B-0020-C100
- Availability:
- In Stock
- Package:
- 100 µg
Description
anti-Polyglutamylation Modification, mAb (GT335) | AG-20B-0020-C100
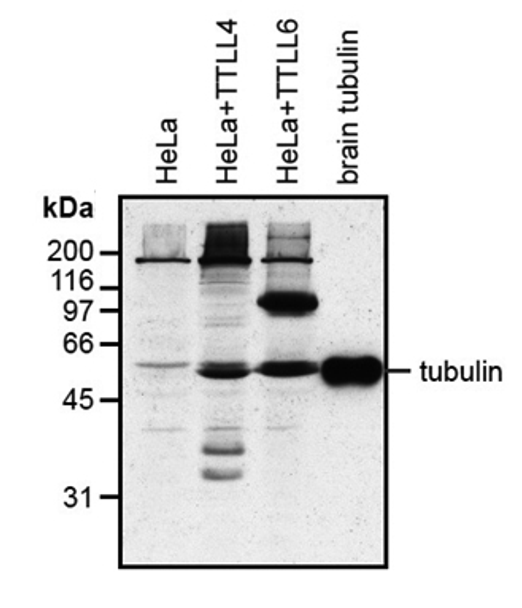
Polyglutamylation is a post-translational modification in which glutamate side chains of variable lengths are formed on the modified protein. It is evolutionarily conserved and the most prominent substrate is tubulin, the microtubule (MT) building block. Polyglutamylation has been proposed to be involved in the functional adaptation of MTs, as it occurs within the carboxy-terminal tubulin tails that participate directly in the binding of many structural and motor MT-associated proteins. The recent identification of new substrates of polyglutamylation indicates that this post-translational modification could be a potential regulator of diverse cellular processes and be involved in cell cycle and cell proliferation.
| Product Details | |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | Polyglutamylated Tubulin; Glutamylated Tubulin; Postranslational Protein Glutamylation |
| Product Type | Monoclonal Antibody |
| Properties | |
| Clone | GT335 |
| Isotype | Mouse IgG1κ |
| Source/Host | Purified from concentrated hybridoma tissue culture supernatant. |
| Immunogen/Antigen | Octapeptide EGEGE*EEG, modified by the addition of two glutamyl units onto the fifth E (indicated by an asterisk). |
| Application |
Electron Microscopy (see Lit. 3) |
| Crossreactivity | All |
| Specificity |
Recognizes the posttranslational modification (poly)glutamylation on proteins. Reacts with polyglutamylated α- and β-tubulin. |
| Purity | ≥95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Purity Detail | Protein G-affinity purified. |
| Concentration | 1mg/ml |
| Formulation | Liquid. In PBS containing 0.02% sodium azide. |