Description
NF-light® (Neurofilament-light) ELISA | UD51001
Milestone in the diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases
The NF-Light® (Neurofilament light) ELISA allows fast (3 hours) quantification of the neurofilament light chain. The assessment requires as little as 50 µL of CSF. Neurofilament light is found to be elevated in neurodegenerative disorders that are associated with the destruction of white matter (substantia alba). Typically these are Parkinson’s disease (PD), Multiple sclerosis (MS) and Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
The assay was developed by UmanDiagnostics, a company focusing on the development of immunochemical tools for fast and accurate determination of neurological and traumatic injuries. The NF-Light® (Neurofilament light) ELISA is exclusively distributed by IBL International.
Neurofilament light helps to differentiate between neurodegenerative brain disorders
Neurofilaments are the backbone of the neuronal cytoskeleton. Inside the axons, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of the neurofilaments regulate, respectively, the expansion and contraction of the microtubules. The neurofilament light (NF-light) chain is the stoichiometrically most common form compared to other isoforms, such as medium and heavy chains. It is rapidly released after axonal destruction and remains highly stable (at least for 8 days, even at room temperature). Moreover, it was found to have significantly higher disease sensitivity and specificity. Due to these special properties neurofilament light is the preferred marker for helping to differentiate between neurodegenerative disorders.
Parkinson’s disease (PD)
The ROC curve below shows that NF-light (red line) can differentiate atypical Parkinson syndromes, such as Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP), Multiple system atrophy (MSA) and Corticobasal degeneration (CBD), from Parkinson’s disease (PD) with high sensitivity.
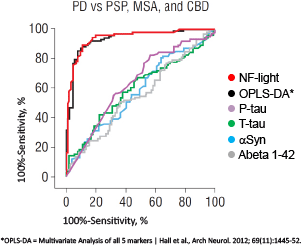
ROC curve from Hall S et al.Accuracy of a panel of 5 cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the differential diagnosis of patients with dementia and/or parkinsonian disorders. Arch Neurol. 2012;69(11):1445-52.
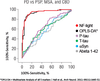
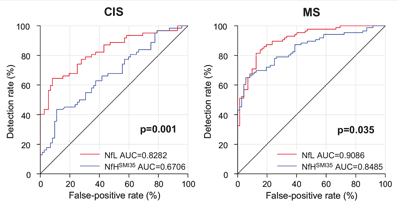
Multiple sclerosis (MS)
The ROC curve below shows that NF-light (red line) has a significantly better discriminatory power than the NF-heavy chain to diagnose Clinically isolated syndrome (CIS) and any other MS-subtype.
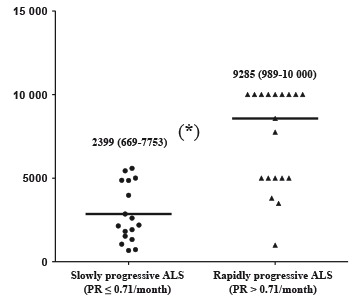
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS)
The graph below shows that NF-light can differentiate rapidly progressive ALS (PR>0.71/month) from slowly progressive ALS (PR≥0.71/month) with high statistical significance (p>0.0001). It was also found that NF-light can help differentiate ALS from other neurodegenerative diseases (data not shown).
Distributed by TECAN, IBL International
For concrete data please consult the Instruction for Use in the download box on the top right side.